Asset Financing with Smart Contract-based Stable Settlements
Money never sleeps.
This blog post introduces asset financing and shows a prototype for Smart Contract-based direct financing settlement on a Stablecoin chain (xDai). This prototype is for demonstration purposes only and not ready for a production setup.
What is Asset Financing?
Asset financing is a type of borrowing related to the assets of a company. In asset financing, the company uses its existing inventory, accounts receivable, or short-term investments to secure short-term financing (source).
The Sample Cases: Accounts Receivable Financing
Accounts receivable represents money owed by entities to the firm on the sale of products or services on credit. (source)
For our example we take accounts receivable for asset financing and a simple Accounts Receivable Purchase transaction. Later samples include a Reverse Factoring transaction. Reverse Factoring is more complex than simple Factoring, but eliminates an important risk, i.e. the so-called verity risk of the Creditor, as we are dealing with a “receiver(Debtor)-confirmed” invoice, ie. not the invoice issuer, but the invoice receiver confirms that she will pay the invoice amount at maturity of the invoice, for example by including it in payment runs in her ERP system.
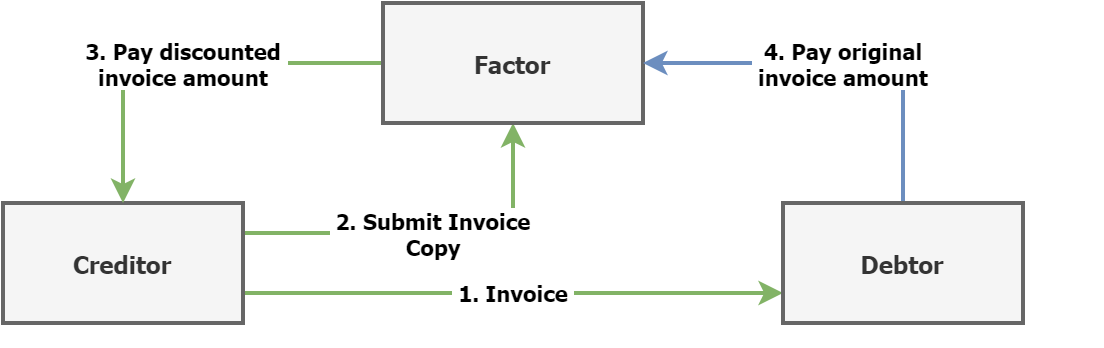
Accounts Receivable Factoring Process Flow
- The Creditor ships products or services to the Debtor and submits an invoice (over USD 101) with typical payment terms (eg. NET-30 for payment in 30 days)
- The Creditor prefers to have USD 100 (1% discount) now instead of USD 101 in 30 days and sends the invoice copy to a Investor
- The Investor purchases the invoice and pays the purchase price amounting to USD 100 to the Creditor/Supplier
- The Debtor pays USD 101 on the original due date (30 days later) to the Investor, the Investor generated a gross profit of 1%
This process flow is highly simplified, but you get the point: the Investor purchases the invoice and receives an interest for this.
Now in real life, this gets messy easily as all the parties probably have different bank accounts. Also the Customer must know that she has to transfer the money not to the Creditor, but to the Investor - or the Investor must have the allowance to debit the Creditor bank account and accept a debt default risk.
Enter Stablecoin Payments
The messy payment part could be avoided very elegant, by using Stablecoin payments. We will show the Ethereum Smart Contract version of the process flow above, which is very simple if based on the native “currency” of the Chain, which is ETH (and Gas) for Ethereum. With running this Smart Contract on the xDai Chain, the native currency is denominated in USD.
Denomination in USD makes the usage far more predictable for B2B use cases.
All payments and settlements - by all parties - are in USD, fully automated, atomic and with no bank accounts involved.
Factoring Process Flow, the Tech Part
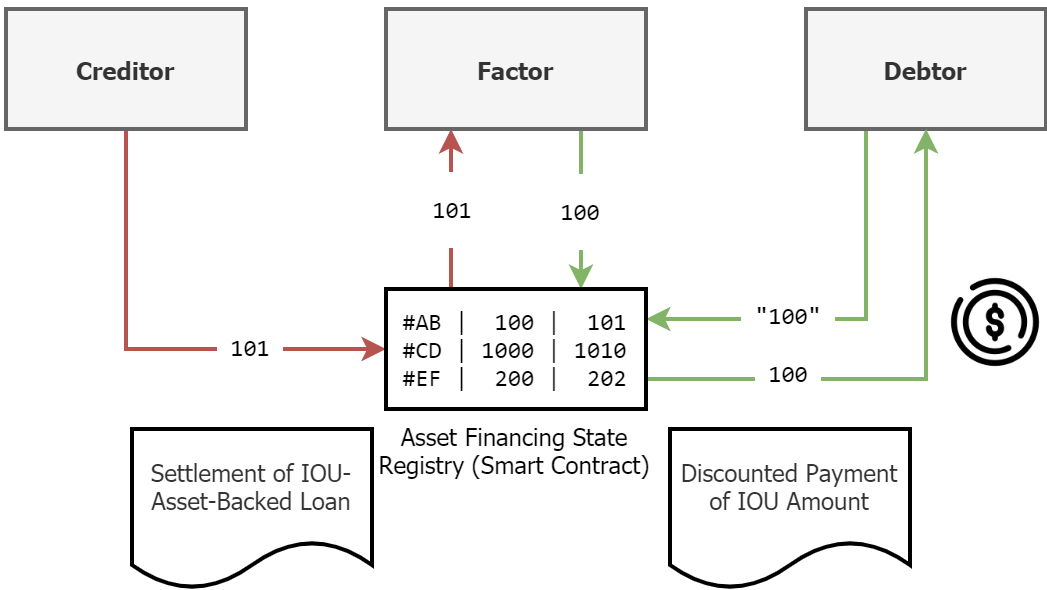
We will go through the steps above in the Solidity code. The complete Smart Contract is here, but be aware it is not even alpha and non-audited!
- Creditor submits invoice to Debtor and registers invoice for financing
This step equals a registration of a uniquely identifiable asset in the Smart Contract that can then be purchased.
function registerAssetForFinancing(bytes32 asset, uint256 amount, uint8 discount) public {
if (financingRegistry[asset].amount > 0) {
revert("Asset already registered or financed.");
}
if ((discount < 0) || (discount > 100)) {
revert("Discount must be between 0% and 100%.");
}
uint256 discountedAmount = amount * discount / 100;
FinancingConditions memory conds = FinancingConditions(
{
amount: amount,
discountedAmount: discountedAmount,
receiver: msg.sender,
financer: address(0x0),
financed: false,
paid: false
});
financingRegistry[asset] = conds;
emit Registered(asset);
}
- Investor pays Creditor and Creditor gets transferred discounted amount (atomic transaction)
The Investor can now send the native currency of the Chain to the Smart Contract and call finance in the same, atomic transaction.
function financeAsset(bytes32 asset) public payable {
if (financingRegistry[asset].amount == 0) {
revert("Asset not registered.");
}
FinancingConditions memory conds = financingRegistry[asset];
if (((conds.amount - conds.discountedAmount) * 10**18) != msg.value) {
revert("Submitted value is not correct.");
}
conds.financed = true;
conds.financer = msg.sender;
financingRegistry[asset] = conds;
conds.receiver.transfer((conds.amount - conds.discountedAmount) * 10**18);
emit Financed(asset);
}
- Debtor pays to the Smart Contract on original due date and the Investor gets transferred the full invoice amount of the Smart Contract (atomic transaction)
function settleFinancedAsset(bytes32 asset) public payable {
if (financingRegistry[asset].amount == 0) {
revert("Asset not registered.");
}
FinancingConditions memory conds = financingRegistry[asset];
if (!conds.financed) {
revert("Asset has not been financed.");
}
if (msg.value != conds.amount * 10**18) {
revert("Submitted value is not Asset amount.");
}
conds.paid = true;
financingRegistry[asset] = conds;
conds.financer.transfer(conds.amount * 10**18);
emit Financed(asset);
}
Recap: Fully Automated Bankless Asset Financing
This post shows how to do a Accounts Receivable Purchase fully automated, bankless and permissionless. What’s the catch?
The xDai Chain has a “market cap” of $1.4 mio. DAI and $14 mio. ERC-20/NFT. This is not really much, especially for B2B applications. The Chain’s operation mode is not permission-less, there are well-known validators which are listed, but this is far away from a permission-less, economic-incentivized, established PoW chain like Ethereum.
So, time will tell if the xDai Chain is “just” a very cool sandbox and prototype environment or if it grows to a risk accessible B2B environment for enterprises and financial players. The Stablecoin native currency is a distinctive feature which xDai surely can build upon.
